Insulin Injection Sites Diagram

How to Use Insulin Injection Sites Properly
There are five doctor recommended insulin injection sites to use when treating diabetes. Rotating evenly between them will give you the highest chances of keeping your tissue in healthy shape. Healthy injection sites mean less pain, faster absorption of insulin, and no bruising, bumps or scar tissue at the injection site.

SubQ Injection
An insulin injection should be given in the subcutaneous tissue or subQ. The subQ is the fatty tissue and is located between the skin and the muscle layer. Injecting the the subQ is the best portion of the body for the insulin to absorb at a proper rate.
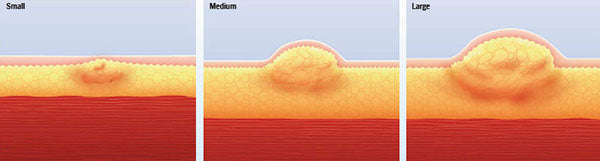
Lipohypertrophy
Over time, repeated injections to the same spot damage the subcutaneous tissue. This damage is called lipohypertrophy. At the beginning of development of lipohypertophy, the injector will start to feel more pain when injecting in that area and light bruising will begin to appear. At this point in time, all injections should be given at least 2 inches away from the damaged tissue. This is necessary to allow the damaged tissue to repair its structure without interference from the injected insulin and needle. Injections should not be given in that location until any bruising, bumps, and pain disappear from the affected injection site. Once the injection site has healed, you can continue to inject in this location.
What happens if you continue to inject in lipohypertrophy?
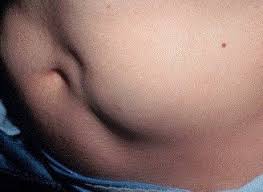
By continuing to use lipohypertrophic areas, you can cause delayed and unpredictable insulin absorption. Take for example your blood sugars are stubbornly high and will not go down. You inject insulin again to speed up the process and then all of a sudden, the insulin that was slow to absorb gets taken up by the blood stream and it stacks with the insulin you just injected, putting you at risk for a dangerous low.

The bumps in the above picture will gradually progress from small to large. The more lipohypertrophy progresses, the longer it takes to heal. In some cases, the lipohypertrophy has permanently damaged the injection site and will not heal. Once lipohypertophy has formed, it will cause erratic absorption of insulin and lead to more difficulty when controlling blood glucose levels. The injector will also feel more pain when inserting the needle and administering insulin in this location.
What do I do if I have lipohyperophy?
If you feel hardness or bumps being formed in a place you frequently inject, it is best to completely avoid this area to let it heal. Depending on the amount of damage, the area should be avoided for 2 to 3 months or more. Over these 2 to 3 months, you should feel the areas to see how the lipohypertrophy is softening and returning back to normal. Before returning to that injection site, there should be no more bumps, bruising, or unnecessary pain when inserting the needle.
Healthy Absorption Rates
In a healthy injection site, once rapid acting insulin is injected, it takes 10-20 minuets to start absorbing. The absorption peaks between 1.5 to 2.5 hours and then ends between 4.5 to 6 hours. An injection site affected by lipohypertrophy has decreased blood flow which can slow insulin absorption by as much as 25%.
How to reach new injection sites?
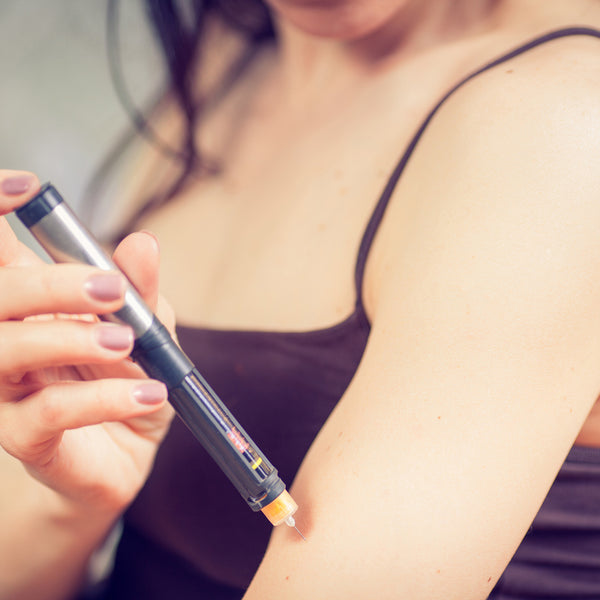

Incorrect Arm Injection
In order to let lipohypertrophy heal, it is necessary to use new injection sites. Injecting in a new location can be scary at first, and you may have to adjust your technique to properly inject. The girl in the above picture is attempting an injection in her arm. Insulin injections should not be given in the bicep as there is less subcutaneous tissue and there is more of a risk for a intramuscular injection.
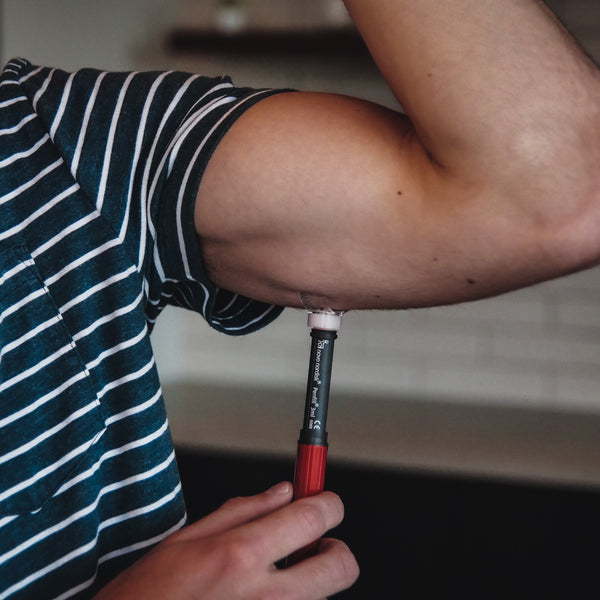

Correct Arm Injection
Instead, insulin injections should be given in the back of the arm. There is more subcutaneous tissue and less of a risk for an intramuscular injection. However, the back of the arm is more difficult to reach than the bicep or front of the arm. Using a device like Steady Shot can make it easy to reach further and use your non-dominant hand to reach a new side of your body.
Common Insulin Injection Questions Answered:
What are the injection sites for insulin?
1) Stomach 2) Back of Arms 3) Back 4) Thighs 5) Buttocks
Why do you rotate injection sites for insulin?
You rotate injection sites for insulin to keep all of your injection sites healthy. Opposed to over using one injection site and damaging the tissue at the injection site.
How to rotate insulin injection sites?
All 5 injection sites on both sides of your body should be used regularly. In order to do this you should be able to inject with your non-dominant hand and practice reaching distant injection sites. You may also use tools designed to help with rotating injection sties such as Steady Shot to make the process easier.
What happens if you don't switch injection sites with insulin?
If you only use one injection site, the tissue at that injection site will get damaged. This damaged tissue will cause more pain when injecting, slow insulin absorption, and cause bruising at the injection site.
What are the best insulin injection sites?
1) Stomach 2) Back of Arms 3) Back 4) Thighs 5) Buttocks
Each location has a different amount of subcutaneous tissue and makeup of internal organs. The stomach usually has plenty of fat depending on the person and great blood flow. The back of the arms have a decent amount of fat and more muscle content which improves blood flow. The buttocks and the thigh tend to have less blood flow and are more fatty areas.
How much insulin absorption is decreased by repeated injection in the same sites?
Absorption of insulin aspart was impaired in lipohypertrophic tissue, yielding a 25% lower Cmax of plasma insulin. When comparing abdominal injections of regular insulin in nine type 1 diabetic patients, it was demonstrated that a 28% greater area under the plasma insulin curve was associated with a more pronounced plasma glucose–lowering effect
How often do you rotate injection sites for insulin?
Injection sites should be rotated with every injection. Ideally every time you inject you should inject in a new body part at least one finger width away from a point you have injected in within the last four weeks.
How to keep track of insulin injection sites?
You can either keep a log of where you injected and on what date or you can keep mental note of where you have been injecting lately. If you start in insert the needle and feel any more pain that usual, stop inserting the needle and find a new injection site with no pain. If you feel no pain when inserting the needle (before administering the insulin) the injection site is healthy.
What insulin's should you rotate injection sites with?
You should rotate all types of insulin from rapid to long acting, and all brands. Stabbing a small piece of metal and injecting anything into the fat will damage the tissue structure. It does not matter what insulin you are using, you should always rotate injection sties to allow ample time for the injection site to heal before next use.
Why do I have red spots around my insulin injection sites?
Red spots at the injection site can be a result of a couple things. It could be due to over injecting in that area. It could also be due to an allergic reaction at the injection site. If the red spots do not go away after a reasonable amount of time, ask your endocrinologist or certified diabetes educator what to do.
Insulin injection sites in abdomen how far from the belly button?
When injecting in the abdomen, rapid acting and long acting insulin should injected at least 2 inches from the belly button.
How to heal insulin injection sites?
The only way to heal insulin injection sites is to not inject in the affected injection site for 2 to 3 months or longer, depending on the severity of the case. During this time, you can check on the bruising, pain, and bumps of at the injection site. Once the symptoms have disappeared, your injection site has healed and you may continue injecting in that area.
Why do insulin injection sites bruise?
Repeated injections in the same area can cause bruising as well as reusing the same needle. A new injection site and a new needle should be used for every injection.
How to deal with insulin resistance at injection sites?
You should avoid injecting in the area with insulin resistance and let it heal back to normal. To make insulin absorb quicker you can warm up the injection site and massage the area to speed up the absorption process.
How do I drop my blood sugar levels faster?
After injecting your insulin, increasing body temperature increases insulin absorption. When liquids are warmed, they move at a faster rate. Blood is liquid so when you take a hot shower or bath, your insulin will begin to absorb quicker and your blood sugars will drop faster.
You can also massage the area where insulin was injected. This will rub the insulin into the tissue and jump start the insulin absorption process.

